SQL is like the universal language for talking to databases, the love language they all understand. It’s used by popular database systems like SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, and PostgreSQL. In this example, we’re focusing on SQL Server. Here are the key commands you’ll want to know. They cover tasks from selecting data to updating records. These commands are your go-to tools for communicating with your database.
Getting Data
1. SELECT
SELECTis your go-to for pulling data out of a table.
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
- Example:
SELECT title, score
FROM posts
WHERE tags LIKE '%python%';
Adding or Changing Data
2. INSERT
- Use
INSERTwhen you need to add new rows to a table.
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2)
VALUES (value1, value2);
- Example:
INSERT INTO users (DisplayName,CreationDate, Reputation, DownVotes, LastAccessDate, Location , UpVotes, Views)
VALUES ('Jane Doe', GETDATE(), 1500, 4,GETDATE(), 'New York', 10, 10);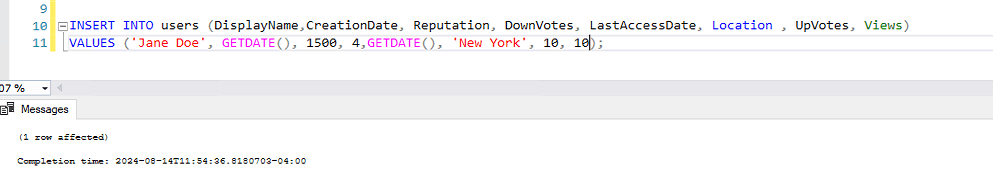
3. UPDATE
UPDATElets you modify existing data in a table.
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1
WHERE condition;
- Example:
UPDATE posts
SET score = 10
WHERE id = 12345
4. DELETE
- When you need to remove rows, use
DELETE.
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
- Example:
DELETE FROM comments
WHERE PostId = 12345;
Managing Tables
5. CREATE
- Use
CREATEto set up a new table from scratch.
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype
);
- Example:
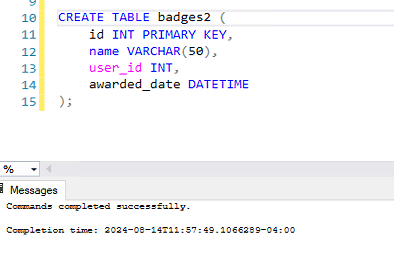
CREATE TABLE badges2 (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50),
user_id INT,
awarded_date DATETIME
);
6. ALTER
ALTERlets you change the structure of an existing table.
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD column_name datatype;
- Example:
ALTER TABLE badges
ADD bio varchar(50);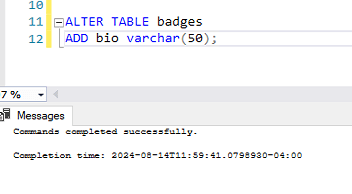
7. DROP
DROPis for deleting a table completely.
DROP TABLE table_name;
- Example:
DROP TABLE badges2;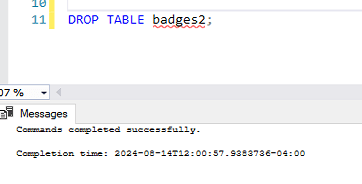
Handling Permissions
8. GRANT
GRANTis how you give users access to the database.
GRANT privilege_name
ON object_name
TO user_name;
- Example:
GRANT SELECT
ON posts
TO guest;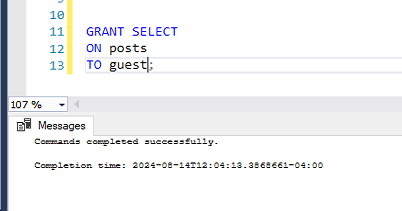
9. REVOKE
- Use
REVOKEto take back access.
REVOKE privilege_name
ON object_name
FROM user_name;
- Example:
REVOKE SELECT
ON posts
FROM guest;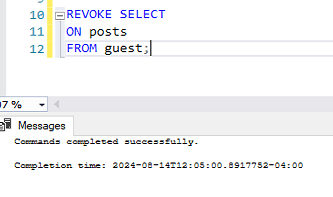
Wrapping Up
These are the main SQL commands you’ll need. Make sure to use the WHERE clause whenever possible, it’s crucial for finding and updating the right data. Without it, you might accidentally slow down the database or delete everything by mistake. So, always double-check that you’ve included it! You’ve been warned.

Leave a comment